. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Such a procedure effectively amounts to a renormalization of the field-dependent determinants produced by gaussian integration.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
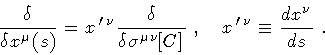
Therefore, the functional wave equation can be written in terms of either type of derivative. Contrary to the statement in ref.[7], area derivatives are regular even when ordinary functional derivatives are not [13].
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .