

Next: 10. Basic Integral for Up: Classical and Quantum Shell Previous:
8. The FGG-method and
9. Hamiltonian for
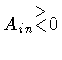 ,
,
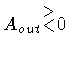
For the sake of notational simplicity, let us set GN=1.
We start with the expression of the momentum in the case6
Ain > 0 and
Aout > 0:
Then, enlisting the equalities
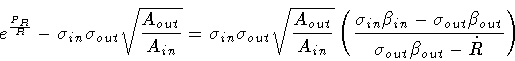 |
(112) |
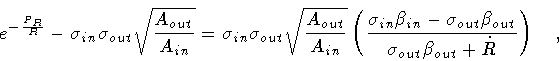 |
(113) |
so that
we find the explicit form of the Hamiltonian quoted in the text
(Eq.55):
![\begin{displaymath}H = \kappa R ^{2}
-
R \left [
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sigm...
... \left( \frac{P_R}{R} \right)
\right ] ^{\frac{1}{2}}
\quad .
\end{displaymath}](img271.gif) |
(116) |
We now repeat the same steps for the case
Ain > 0 and
Aout < 0. Letting
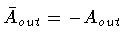 ,
we find
,
we find
Enlisting now the equalities
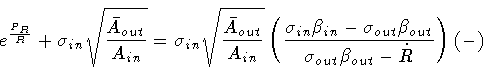 |
(118) |
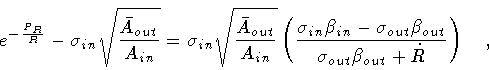 |
(119) |
so that
we find
![\begin{displaymath}H = \kappa R ^{2} -
R \left [
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sigma...
... \left( \frac{P_R}{R} \right)
\right ] ^{\frac{1}{2}}
\quad .
\end{displaymath}](img284.gif) |
(122) |
Evidently, we can follow the same procedure in the cases
Ain < 0,
Aout < 0;
Ain < 0,
Aout > 0.
The corresponding expressions are
![$\displaystyle H = \kappa R ^{2} -
R \left [
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sqrt{A_{in} A_{out}}
\cosh \left( \frac{P_R}{R} \right)
\right ] ^{\frac{1}{2}}$](img285.gif) |
|
|
(123) |
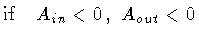 |
|
|
|
![$\displaystyle H = \kappa R ^{2} -
R \left [
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sigma _{out} \sqrt{- A_{in} A_{out}}
\sinh \left( \frac{P_R}{R} \right)
\right ] ^{\frac{1}{2}}$](img287.gif) |
|
|
(124) |
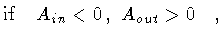 |
|
|
|
or, in a more compact notation
| H |
= |
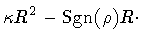 |
|
| |
|
![$\displaystyle \cdot
\left[\,
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sigma _{in} \sigma _{out}
\l...
...\vert A_{in} A_{out} \vert}
}
}
\right) ^{\frac{1}{2}}
\right] ^{\frac{1}{2}}
.$](img290.gif) |
(125) |
The Hamiltonian for the shell of dust quoted in Section IV can be
derived along the same steps with little change, and one obtains
| H |
= |
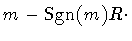 |
|
| |
|
![$\displaystyle \cdot
\left[\,
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sigma _{in} \sigma _{out}
\l...
...\vert A_{in} A_{out} \vert}
}
}
\right) ^{\frac{1}{2}}
\right] ^{\frac{1}{2}}
.$](img290.gif) |
(126) |


Next: 10. Basic Integral for Up: Classical and Quantum Shell Previous:
8. The FGG-method and
Stefano Ansoldi
Department of Theoretical Physics
University of Trieste
TRIESTE - ITALY
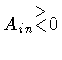 ,
,
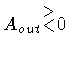
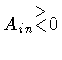 ,
,
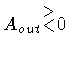
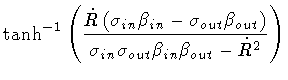
![$\displaystyle \frac{1}{2} \ln \left [
\frac{
\left(
\sigma _{in} \beta _{in}-\d...
...
\dot{R}
\right)
\left(
\sigma _{out} \beta _{out}
-
\dot{R}
\right)
}
\right ]$](img261.gif)
![$\displaystyle \ln \left [
\frac{
\left(
\sigma _{in} \beta _{in} - \dot{R}
\rig...
...ft(
\sigma _{out} \beta _{out} + \dot{R}
\right) ^{2}
}
\right ] ^{\frac{1}{2}}$](img262.gif)
![$\displaystyle \ln \left [
\sqrt{\frac{A_{out}}{A_{in}}}
\frac{\vert \sigma _{in...
...n} - \dot{R} \vert}
{\vert \sigma _{out} \beta _{out} - \dot{R} \vert}
\right ]$](img263.gif)
![$\displaystyle \ln \left [
\sqrt{\frac{A_{out}}{A_{in}}}
\frac{
\left(
\sigma _{...
...
{
\left(
\sigma _{out} \beta _{out} - \dot{R}
\right)
\sigma _{out}
}
\right ]$](img264.gif)
![$\displaystyle \ln \left [
\sigma _{in} \sigma _{out}
\sqrt{\frac{A_{out}}{A_{in...
...} \beta _{in} - \dot{R}}
{\sigma _{out} \beta _{out} - \dot{R}}\right ]
\quad .$](img265.gif)
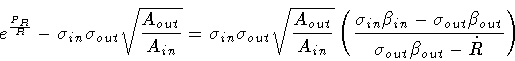
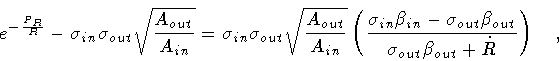
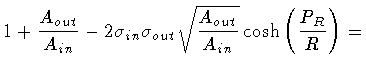
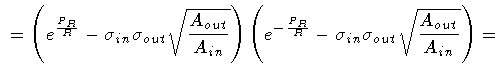
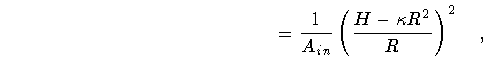
![\begin{displaymath}H = \kappa R ^{2}
-
R \left [
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sigm...
... \left( \frac{P_R}{R} \right)
\right ] ^{\frac{1}{2}}
\quad .
\end{displaymath}](img271.gif)
![]() ,
we find
,
we find
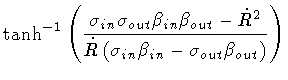
![$\displaystyle \frac{1}{2} \ln \left [
\frac{
\left(
\sigma _{in} \beta _{in} - ...
...ta _{in}
\right)
\left(
\dot{R} - \sigma _{out} \beta _{out}
\right)
}
\right ]$](img274.gif)
![$\displaystyle \ln \left [
\frac{
\left(
\sigma _{in} \beta _{in} - \dot{R}
\rig...
...\sigma _{out} \beta _{out} - \dot{R}
\right) ^{2}
}
(-)
\right ] ^{\frac{1}{2}}$](img275.gif)
![$\displaystyle \ln \left [
\sqrt{\frac{\bar{A} _{out}}{A_{in}}}
\frac{
\left\ver...
...vert
}
{
\left\vert \sigma _{out} \beta _{out} - \dot{R} \right\vert
}
\right ]$](img276.gif)
![$\displaystyle \ln \left [
\sqrt{\frac{\bar{A} _{out}}{A_{in}}}
\frac{
\left( \s...
... _{in}
}
{
\left( \sigma _{out} \beta _{out} - \dot{R} \right) ( - )
}
\right ]$](img277.gif)
![$\displaystyle \ln \left [
- \sigma _{in} \sqrt{\frac{\bar{A} _{out}}{A_{in}}}
\...
... \beta _{in} - \dot{R}}
{\sigma _{out} \beta _{out} - \dot{R}}
\right ]
\quad .$](img278.gif)
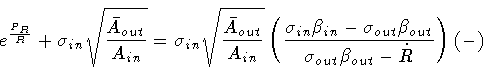
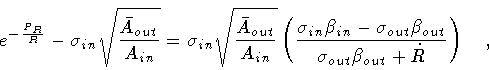
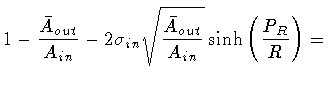
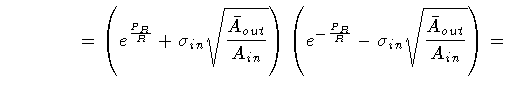
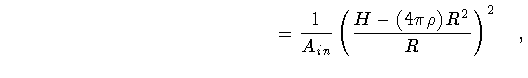
![\begin{displaymath}H = \kappa R ^{2} -
R \left [
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sigma...
... \left( \frac{P_R}{R} \right)
\right ] ^{\frac{1}{2}}
\quad .
\end{displaymath}](img284.gif)
![$\displaystyle H = \kappa R ^{2} -
R \left [
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sqrt{A_{in} A_{out}}
\cosh \left( \frac{P_R}{R} \right)
\right ] ^{\frac{1}{2}}$](img285.gif)
![$\displaystyle H = \kappa R ^{2} -
R \left [
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sigma _{out} \sqrt{- A_{in} A_{out}}
\sinh \left( \frac{P_R}{R} \right)
\right ] ^{\frac{1}{2}}$](img287.gif)
![$\displaystyle \cdot
\left[\,
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sigma _{in} \sigma _{out}
\l...
...\vert A_{in} A_{out} \vert}
}
}
\right) ^{\frac{1}{2}}
\right] ^{\frac{1}{2}}
.$](img290.gif)
![$\displaystyle \cdot
\left[\,
A_{in} +
A_{out} -
2 \sigma _{in} \sigma _{out}
\l...
...\vert A_{in} A_{out} \vert}
}
}
\right) ^{\frac{1}{2}}
\right] ^{\frac{1}{2}}
.$](img290.gif)